
Banks and credit unions must report currency transactions exceeding $10,000, whether they involve deposits, withdrawals, or the exchange of currency.Who Is Required to Submit Currency Transaction Reports?Ī wide range of financial businesses are subject to CTR reporting obligations, including: FinCEN operates the Bank Secrecy Act E-Filing System, which streamlines the submission process.įor additional information on the history of compliance legislation and requirements view our timeline of key BSA/AML regulations. Today, electronic filing makes it easier for businesses to submit CTRs. For instance, the USA PATRIOT Act of 2001 expanded the definition of financial institutions subject to CTR reporting and introduced new anti-money laundering requirements.ĬTRs were once paper forms that had to be filled in and sent to FinCEN. Over the years, amendments and new regulations were introduced to strengthen CTRs and adapt to changing threats and technologies. Over time, the scope of reportable transactions expanded to include additional types of businesses, institutions, and instruments.Īs financial crimes evolved and became more sophisticated, so did the CTR requirements.

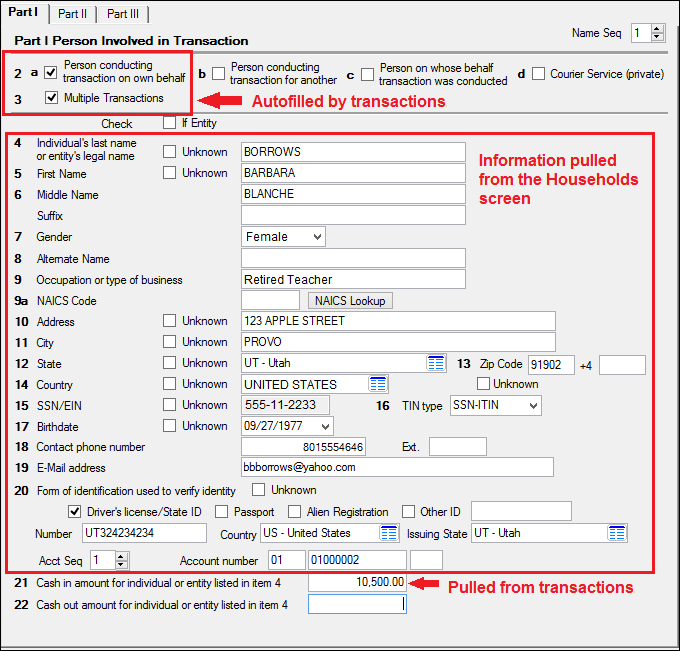
Initially, banks were only required to report transactions involving cash or negotiable instruments of more than $10,000. The BSA introduced the concept of CTRs as a means to monitor large cash transactions, which were often associated with illegal activities such as drug trafficking, organized crime, and tax evasion. They often declined to do so to protect the privacy of their customers. Prior to the BSA, law enforcement agencies relied on banks to voluntarily report suspicious activity. This practice is called structuring, and banks are obligated to file a SAR if they suspect a customer is attempting to structure their transactions in this way.ĬTRs were first introduced in the Bank Secrecy Act of 1970 (BSA). It is illegal for customers to attempt to circumvent reporting by splitting the money into multiple transactions with amounts smaller than the reporting threshold. For example, if they initially ask to deposit $11,000 but then decide to deposit $9,500 or abandon the transaction, the bank will submit a CTR and a Suspicious Activity Report (SAR). The CTR form requires information such as the account number and verified customer identity information, which is one reason banks and financial services businesses are required to collect identifying information from customers in the first place.īanks must also submit a CTR when a customer requests a transaction over the threshold but then changes their mind. For example, whenever a bank customer deposits, withdraws, or transfers more than $10,000 in one day - or makes multiple transactions amounting to $10,000 - a bank must send a CTR to FinCEN. What Are Currency Transaction Reports (CTRs)?ĬTRs are reports that financial institutions must file with the Financial Crimes Enforcement Network (FinCEN), detailing transactions involving cash or other currency exceeding $10,000. They play a crucial role in detecting and preventing money laundering, terrorist financing, and other illicit activities.
As such, financial institutions are required to comply with anti-money laundering (AML) regulations and provide financial information to identify and discourage money laundering and financial crime.Ĭurrency transaction reports (CTR) are among the most widely used and effective AML reporting tools. This process is known as the placement stage and is the first of three stages of money laundering. Financial institutions are often the point at which illegitimately earned money enters the financial system.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
